How To A Mac App With Sudo
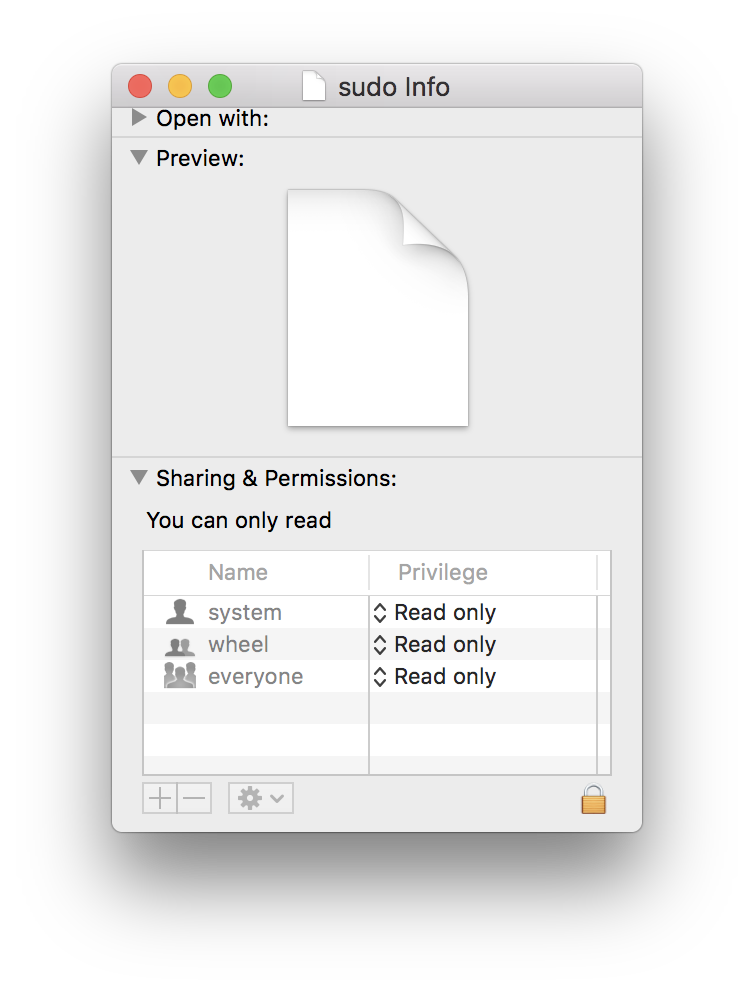
Editing some files on an OS X system requires superuser or root permissions. Typically, this is accomplished using sudo (which lets authorized users assume superuser powers, cape and tights optional) and vi. To the uninitiated, vi can cause intestinal distress and hair loss. An alternative is the use of TextEdit, the graphical text editor application. Sudo nvram StartupMute=%00 A word about ‘sudio’ The sudo part of that command means that it will be run at the level of a “superuser” on your Mac, with extra abilities, permissions and risks. A flaw with the Sudo command used in macOS Terminal let non-privileged users and programs run commands as Root. It was patched in version 1.8.31 which was released with macOS High Sierra 10.13.6. Sudo -s is far easier than enabling the root user since it just starts up a shell with root permissions as a one step, on demand action. Not only is it fast, but it doesn't need to be reconfigured when you don't need the root user and doesn't expose the server to any more risk or vulnerability that adding a root user would entail.
These advanced steps are primarily for system administrators and others who are familiar with the command line. You don't need a bootable installer to upgrade macOS or reinstall macOS, but it can be useful when you want to install on multiple computers without downloading the installer each time.
From now on you’ll be able to move files to your drive and edit them in place from a Mac or PC. Use a third-party app. Sudo nano /etc/fstab. Check Sudo Secure Path. To fix this, we need to add the directory containing our scripts in the sudo securepath by using the visudo command by editing /etc/sudoers file as follows. $ sudo visudo Attention: This method has serious security implications especially on servers running on the Internet. With this you always do sudo -A command. The -A argument tells sudo to execute a command that echos the password to stdout. That command is something you write. For this explaination let's call the command pw and stick it /usr/local/bin. So it's full pathname would be /usr/local/bin/pw. Sudo -A can get the pathname to pw a number of ways.
What you need to create a bootable installer
- A USB flash drive or other secondary volume, formatted as Mac OS Extended, with at least 12GB of available storage
- A downloaded installer for macOS Big Sur, Catalina, Mojave, High Sierra, or El Capitan
Download macOS
- Download: macOS Big Sur, macOS Catalina, macOS Mojave, or macOS High Sierra
These download to your Applications folder as an app named Install macOS [version name]. If the installer opens after downloading, quit it without continuing installation. To get the correct installer, download from a Mac that is using macOS Sierra 10.12.5 or later, or El Capitan 10.11.6. Enterprise administrators, please download from Apple, not a locally hosted software-update server. - Download: OS X El Capitan
This downloads as a disk image named InstallMacOSX.dmg. On a Mac that is compatible with El Capitan, open the disk image and run the installer within, named InstallMacOSX.pkg. It installs an app named Install OS X El Capitan into your Applications folder. You will create the bootable installer from this app, not from the disk image or .pkg installer.
Use the 'createinstallmedia' command in Terminal
- Connect the USB flash drive or other volume that you're using for the bootable installer.
- Open Terminal, which is in the Utilities folder of your Applications folder.
- Type or paste one of the following commands in Terminal. These assume that the installer is in your Applications folder, and MyVolume is the name of the USB flash drive or other volume you're using. If it has a different name, replace
MyVolumein these commands with the name of your volume.
Big Sur:*
Mac Os Sudo
Catalina:*
How To A Mac App With Sudoku
Mojave:*
High Sierra:*
El Capitan:
* If your Mac is using macOS Sierra or earlier, include the --applicationpath argument and installer path, similar to the way this is done in the command for El Capitan.
After typing the command:
- Press Return to enter the command.
- When prompted, type your administrator password and press Return again. Terminal doesn't show any characters as you type your password.
- When prompted, type Y to confirm that you want to erase the volume, then press Return. Terminal shows the progress as the bootable installer is created.
- When Terminal says that it's done, the volume will have the same name as the installer you downloaded, such as Install macOS Catalina. You can now quit Terminal and eject the volume.
Use the bootable installer
How To Sudo On Mac
After creating the bootable installer, follow these steps to use it:
- Plug the bootable installer into a Mac that is connected to the internet and compatible with the version of macOS you're installing.
- Press and hold the Option (Alt) ⌥ key immediately after turning on or restarting your Mac.
- Release the Option key when you see a dark screen showing your bootable volumes.
If you can't start up from the bootable installer, make sure that the External Boot setting in Startup Security Utility is set to allow booting from external media. - Choose your language, if prompted.
- Select Install macOS (or Install OS X) from the Utilities window, then click Continue and follow the onscreen instructions.
Learn more
For more information about the createinstallmedia command and the arguments that you can use with it, make sure that the macOS installer is in your Applications folder, then enter the appropriate path in Terminal:
How To Use Sudo

- Big Sur: /Applications/Install macOS Big Sur.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia
- Catalina: /Applications/Install macOS Catalina.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia
- Mojave: /Applications/Install macOS Mojave.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia
- High Sierra: /Applications/Install macOS High Sierra.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia
- El Capitan: /Applications/Install OS X El Capitan.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia